When it comes to sunscreen, SPF plays a crucial role in protecting your skin from harmful UVB rays. The debate of SPF 30 vs SPF 50 is common, but how much do they actually differ?
SPF 30 blocks up to 97% of UVB rays.
SPF 50 stops up to 98% of UVB rays.
This 1% difference in SPF 30 vs SPF 50 might seem small, but it can matter if you have sensitive skin or spend long hours outdoors. Choosing the right SPF depends on factors like your skin type, activity level, and the intensity of sun exposure in your environment.
What Is SPF and Its Role in Sun Protection
Defining SPF: Sun Protection Factor
SPF, or sun protection factor, measures how well a sunscreen protects your skin from UVB rays. These rays are responsible for sunburn and play a significant role in skin cancer development. The SPF value is calculated by comparing the amount of UV energy needed to cause redness on protected skin versus unprotected skin. For example, an SPF 30 sunscreen allows you to stay in the sun 30 times longer without burning than if you wore no sunscreen.
SPF is not just a number; it’s a critical tool for shielding your skin from harmful UV rays. Regular use of sunscreen has been shown to reduce the risk of squamous cell carcinoma by up to 40% over four years.
How SPF Protects Against UVB Rays
Sunscreens with SPF act as a barrier, either absorbing or reflecting UVB rays before they can damage your skin. Research highlights that certain ingredients, like Methylene Blue, effectively filter UVB rays, reducing DNA damage and promoting skin cell repair. While SPF 30 blocks about 97% of UVB rays, SPF 50 increases this to 98%. This small difference can be vital for sensitive skin or prolonged sun exposure.
Importance of UVA Protection in Sunscreen
While SPF focuses on UVB rays, UVA rays also pose a threat. They penetrate deeper into your skin, causing premature aging and contributing to skin cancer. A broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both UVA and UVB rays, offering more comprehensive sun protection. Studies show that sunscreens with high UVA protection prevent pigmentation and reduce the risk of actinic keratoses, a precursor to skin cancer.
Evidence Type | Findings | Implications |
|---|---|---|
Biological Effects | Linked to skin cancer and photoaging. | |
Clinical Impact | Balanced sunscreen reduces UV-induced damage. | Highlights the need for UVA/UVB protection. |
Long-term Study | High UVA-PF sunscreen prevents skin cancers. | Supports the importance of UVA protection. |
Using a broad-spectrum sunscreen ensures effective sun protection against both UVA and UVB rays, keeping your skin healthier in the long run.
SPF 30 vs SPF 50: Understanding the Difference

UVB Protection Percentages: 97% vs 98%
The difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50 lies in how much UVB radiation they block. SPF 30 filters out 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks 98%. This 1% difference may seem small, but it can make a big impact, especially if you have sensitive skin or spend extended time outdoors.
SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays.
SPF 50 blocks 98% of UVB rays.
This slight increase in protection means fewer harmful rays reach your skin, reducing the risk of sunburn and long-term damage. For those with fair or sun-sensitive skin, even a 1% improvement can provide significant protection against UVB rays.
Duration of Protection: Does SPF 50 Last Longer?
SPF ratings also indicate how long sunscreen can protect your skin before reapplication is needed. The higher the SPF, the longer you can stay in the sun without burning. For example:
SPF Rating | UVB Protection | Time Before Burning (10 min burn time) |
|---|---|---|
SPF 30 | 97% | |
SPF 50 | 98% | 500 minutes (8.3 hours) |
If your skin typically burns after 10 minutes of sun exposure, SPF 30 extends that time to 300 minutes, while SPF 50 increases it to 500 minutes. However, this doesn’t mean you should skip reapplying sunscreen. Sweat, water, and physical activity can reduce its effectiveness. Dermatologists recommend reapplying every two hours, regardless of the SPF level.
Skin Sensitivity and Choosing Higher SPF Levels
Your skin type plays a key role in deciding between SPF 30 and SPF 50. People with sensitive skin or conditions like rosacea benefit more from the added protection of SPF 50. Studies show that 49.6% of sun-sensitive individuals experience better results with higher SPF levels, compared to 22.1% of those without sensitivity.
Group | Percentage | Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
Sun-Sensitive | 49.6 | 48.6 – 50.7 |
Not Sun-Sensitive | 22.1 | 21.1 – 23.1 |
If you have darker skin or don’t burn easily, SPF 30 may suffice for daily use. However, for prolonged exposure, such as a beach day or hiking trip, SPF 50 offers more reliable protection. Always consider your environment and activity level when choosing sunscreen.
Tip: Pair sunscreen with other protective measures like hats and sunglasses for the best defense against harmful UV rays.
Common Misconceptions About SPF Levels
Higher SPF Does Not Mean Unlimited Protection
Many people believe that higher SPF sunscreens offer unlimited protection from the sun. This is not true. SPF measures how much UVB radiation is blocked, but it does not account for UVA rays, which penetrate deeper into your skin. Broad-spectrum sunscreens are essential because they protect against both UVA and UVB rays. Research shows that blocking only UVB rays leaves your skin vulnerable to damage caused by UVA exposure, including premature aging and increased skin cancer risk.
Even high-SPF sunscreens have limits. Studies reveal that sunscreens with SPF 70 or higher provide adequate protection even when applied in smaller amounts. However, this does not mean you can skip proper application or reapplication. Sunscreen effectiveness depends on how much you apply and how often you reapply it.
SPF 50 Is Not Twice as Effective as SPF 30
The difference between SPF 30 and SPF 50 is often misunderstood. SPF 50 does not offer double the protection of SPF 30. Instead, SPF 30 blocks 97% of UVB rays, while SPF 50 blocks 98%. This 1% difference may seem minor, but it can make a significant impact during prolonged sun exposure or for individuals with sensitive skin.
High-SPF sunscreens can provide better protection when applied in lower amounts, but this does not mean SPF 50 is vastly superior to SPF 30. Both options require proper application to achieve their intended effectiveness.
Sunscreen Needs Reapplication Regardless of SPF
Another common misconception is that higher SPF sunscreens do not need reapplication. This is false. Sunscreen wears off due to sweat, water, and friction from clothing or sand. Studies show that contact with sand can reduce sunscreen’s protective effect by up to 60%, even after it has dried.
Dermatologists recommend reapplying sunscreen every two hours, regardless of its SPF level. Many people fail to apply the recommended amount, which reduces the actual SPF protection. Research indicates that only 4% of users follow proper application guidelines. To maximize protection and reduce skin cancer risk, you should reapply sunscreen frequently, especially during outdoor activities.
Tip: Pair sunscreen with hats, sunglasses, and protective clothing for comprehensive sun protection.
Choosing Between SPF 30 and SPF 50
Factors to Consider: Skin Type, Activity, and Environment
Choosing between SPF 30 and SPF 50 depends on several personal and environmental factors. Your skin type plays a significant role. If you have fair or sensitive skin, SPF 50 may offer better protection against harmful UVB rays. For darker skin tones, SPF 30 often provides sufficient coverage for daily use.
Your activity level also matters. If you engage in outdoor sports, swimming, or other activities that cause sweating, you’ll need a sunscreen that stays effective despite physical exertion. Studies show that physical activity and water exposure reduce SPF stability, making reapplication essential every two hours.
Environmental conditions further influence your choice. High-altitude locations or areas with intense sunlight increase your risk of sunburn. In such cases, SPF 50 offers an added layer of protection. A clinical study highlights that outdoor workers exposed to varying climates benefit from sunscreens designed for prolonged sun exposure.
Study Title | Focus | Findings |
|---|---|---|
New methods for assessing secondary performance attributes of sunscreens | Environmental factors | Different criteria are needed for sunscreen efficacy in outdoor settings. |
Sun protection factor persistence during a day with physical activity | Physical activity | Physical activity and bathing reduce SPF stability, requiring reapplication. |
When SPF 50 Is Better for Sun Protection
SPF 50 is ideal for situations where sun exposure is prolonged or intense. If you’re spending a day at the beach, hiking, or working outdoors, the extra 1% UVB protection can make a difference. Clinical studies reveal that SPF 50 reduces the risk of sunburn by 55.3% compared to lower SPF levels.
SPF Level | Effectiveness Against Sunburn | Study Reference |
|---|---|---|
SPF 50+ | ||
SPF 100+ | 5% more sunburned | |
SPF 100+ | Significantly less erythema |
Additionally, SPF 50 is better suited for individuals with sensitive skin or those prone to conditions like rosacea. Dermatologists often recommend higher SPF levels for these groups to minimize the risk of skin damage.
Balancing SPF with Other Sun Protection Measures
While SPF 30 and SPF 50 provide excellent UVB protection, sunscreen alone isn’t enough for complete sun safety. Combining sunscreen with other protective measures enhances your defense against harmful rays.
Wear wide-brimmed hats to shield your face and neck.
Use UV-blocking sunglasses to protect your eyes.
Opt for lightweight, long-sleeved clothing to cover exposed skin.
Seek shade during peak sunlight hours, typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
A broad-spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB rays is essential. However, reapplication remains critical. Sweat, water, and physical activity reduce sunscreen effectiveness, even with higher SPF levels.
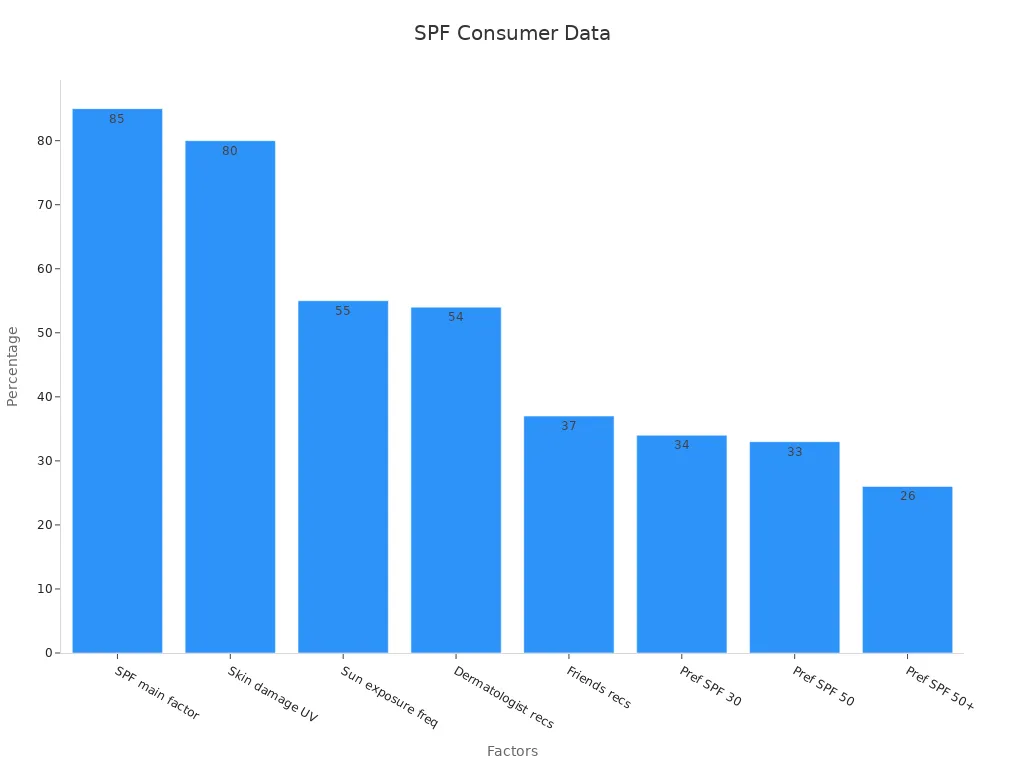
Consumer research shows that 85% of people prioritize SPF levels when choosing sunscreen. However, only 34% prefer SPF 30, while 33% opt for SPF 50. This indicates that many individuals weigh other factors, such as skin type and activity level, when making their decision.
Factor Influencing SPF Choice | Percentage of Respondents |
|---|---|
SPF level is the main factor | 85% |
Concerns about skin damage from UV rays | 80% |
Frequency of sun exposure | 55% |
Recommendations from dermatologists | 54% |
Recommendations from friends/family | 37% |
Preference for SPF 30 | 34% |
Preference for SPF 50 | 33% |
Preference for SPF 50+ | 26% |
By balancing SPF with other sun protection measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of sunburn, premature aging, and skin cancer.
Tips for Effective Sunscreen Use

How Much Sunscreen to Apply
Knowing how to apply sunscreen correctly is essential for effective protection. Experts recommend using about one ounce of sunscreen—roughly the size of a golf ball—to cover your entire body. For your face and neck, use a nickel-sized amount. Applying too little reduces the SPF level, leaving your skin vulnerable to UV damage.
To make sunscreen application a daily habit, consider placing it next to your toothpaste. Studies show this simple trick increases usage by 26%. For outdoor activities, choose an SPF 50 sunscreen for better coverage, while SPF 30 works well for daily use. If you have darker skin, tinted sunscreens can block visible light and provide additional benefits.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Habit Formation | Placing sunscreen next to toothpaste increased usage by 26%. |
SPF Recommendations | Use SPF greater than 30 for daily use and at least 50 for outdoor activities. |
Tinted Sunscreens | Recommended for individuals with darker skin types to block visible light. |
When and How Often to Reapply
Reapplying sunscreen every two hours ensures continuous protection, especially during outdoor activities. Sweat, water, and physical activity reduce its effectiveness over time. For indoor workers, applying sunscreen once in the morning may suffice, as studies show it remains effective for several hours. However, outdoor workers should reapply frequently to maintain protection.
Aspect | Findings |
|---|---|
Indoor Workers | Sunscreen applied once in the morning remains effective for several hours. |
Efficacy Reduction at 2 hrs | Mean peak reduction of 16.3%. |
Efficacy Reduction at 8 hrs | Total reduction of 28.2% by the end of the workday. |
Reapplication Recommendation | May be unnecessary for indoor workers if adequate amount is applied once. |
Outdoor Recommendation | Reapplication every two hours is recommended by the American Academy of Dermatology. |
Complementary Sun Protection: Hats, Clothing, and Shade
Sunscreen alone cannot provide complete protection. Combining it with other measures enhances your defense against harmful UV rays. Wearing wide-brimmed hats shields your face and neck, while UV-blocking sunglasses protect your eyes. Long-sleeved shirts and pants offer excellent coverage, reducing the need for frequent sunscreen reapplication.
Protective clothing, such as long sleeves and wide-brimmed hats, minimizes UV exposure.
Seeking shade during peak sunlight hours lowers your risk of sunburn.
Covering up with clothing is often more convenient than applying sunscreen.
The Surgeon General emphasizes the importance of increasing shade availability in outdoor spaces to prevent skin cancer. By pairing sunscreen with these measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of sun damage.
Oully’s Expertise in Sun Protection Products
Custom Formulation for SPF Products
Oully specializes in creating custom sunscreen formulations tailored to your brand’s needs. You can choose from a wide range of SPF levels, textures, and ingredients to match your target audience. Whether you want lightweight, fast-absorbing formulas or water-resistant options, Oully’s team ensures every product meets high standards of quality and performance.
The company uses advanced research and technology to develop sunscreens that protect against both UVA and UVB rays. You can also opt for additional features like tinted formulas for darker skin tones or reef-safe ingredients for eco-conscious consumers. With Oully’s expertise, your brand can offer innovative products that stand out in the competitive sunscreen market.
Tip: Custom formulations allow you to cater to specific customer preferences, such as sensitive skin or outdoor activities.
Sustainable Practices in Sunscreen Manufacturing
Oully prioritizes sustainability in every step of its manufacturing process. The company uses eco-friendly ingredients and packaging to reduce environmental impact. Reef-safe sunscreens, which avoid harmful chemicals like oxybenzone and octinoxate, are a key focus. These products protect marine ecosystems while providing effective sun protection.
The sunscreen industry is shifting toward greener practices. Sales of reef-safe sunscreens have grown by 27% annually in the U.S., and 66% of global consumers are willing to pay more for sustainable products. The market for natural personal care products is projected to reach $25 billion by 2025.
Market Segment | Share (2023) | Projected Growth (2025) |
|---|---|---|
Conventional Sunscreens | 80% | 4% CAGR |
Reef-Safe and Mineral Sunscreens | 20% | 15% CAGR |
By choosing Oully, you align your brand with these growing trends, appealing to environmentally conscious customers.
Supporting Brands with End-to-End Solutions
Oully offers comprehensive support to help you bring your sunscreen products to market. From formulation and packaging design to manufacturing and dropshipping, the company handles every step of the process. You can rely on Oully’s FDA-, ISO-, and cGMP-certified facility to produce high-quality sunscreens that meet global standards.
Flexible low MOQ options and fast production turnaround make it easier for you to launch new products or expand your existing line. Oully’s dropshipping services ensure efficient delivery to your customers, saving you time and resources.
With Oully’s end-to-end solutions, you can focus on growing your brand while leaving the technical details to the experts.
SPF 30 and SPF 50 both play an essential role in protecting your skin from harmful UV rays. While SPF 50 offers slightly more coverage, your choice should depend on your skin type, activity level, and time spent outdoors. Incorporating sun safety into your daily routine can significantly reduce your risk of skin damage and serious conditions like melanoma.
Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher is vital for maintaining healthy skin.
Nearly 90% of melanoma cases are linked to sun exposure, emphasizing the importance of consistent protection.
Regular application of SPF 30 can lower the risk of skin cancers like basal cell carcinoma.
By combining sunscreen with other measures like hats and shade, you can create a comprehensive sun safety strategy that keeps your skin healthy and protected.
FAQ
What does SPF actually mean?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor. It measures how much UVB radiation sunscreen blocks. For example, SPF 30 lets you stay in the sun 30 times longer without burning compared to no sunscreen. Higher SPF levels provide slightly more protection but don’t block 100% of UV rays.
Does SPF 50 last longer than SPF 30?
No, SPF doesn’t determine how long sunscreen lasts. Both SPF 30 and SPF 50 need reapplication every two hours. Sweat, water, and physical activity reduce effectiveness. Always reapply sunscreen regularly to maintain protection, regardless of its SPF level.
Can I skip sunscreen if I wear protective clothing?
No, sunscreen complements protective clothing. UV rays can still reach exposed areas like your face and hands. Combine sunscreen with hats, sunglasses, and long sleeves for better protection. This approach reduces your risk of sunburn and long-term skin damage.
Is SPF 50 better for sensitive skin?
Yes, SPF 50 offers slightly more UVB protection, which benefits sensitive skin. If you have conditions like rosacea or burn easily, higher SPF levels reduce the risk of irritation. Pair SPF 50 with broad-spectrum sunscreen to shield against UVA rays as well.
Do I need sunscreen on cloudy days?
Yes, UV rays penetrate clouds. Up to 80% of UV radiation reaches your skin even on overcast days. Apply sunscreen daily, regardless of weather, to protect against sunburn and skin damage. Broad-spectrum sunscreen ensures coverage against both UVA and UVB rays.
















